So except in the 3 areas that matter most. Got it.
I wouldn’t describe them as “3 areas that matter most” — shipping and aviation are only part of transport

Note that this chart only runs through 2020
Nice insight, thank you. I wonder if the electricity industry uses is under the industry umbrella or the electricity and heating umbrella. Separate entities of course, but I’d be interested in seeing how electricity consumption compares from industry to consumer sectors.
Not in this chart. I’ve seen national inventories which distribute electric sector emissions out to the consumers of it
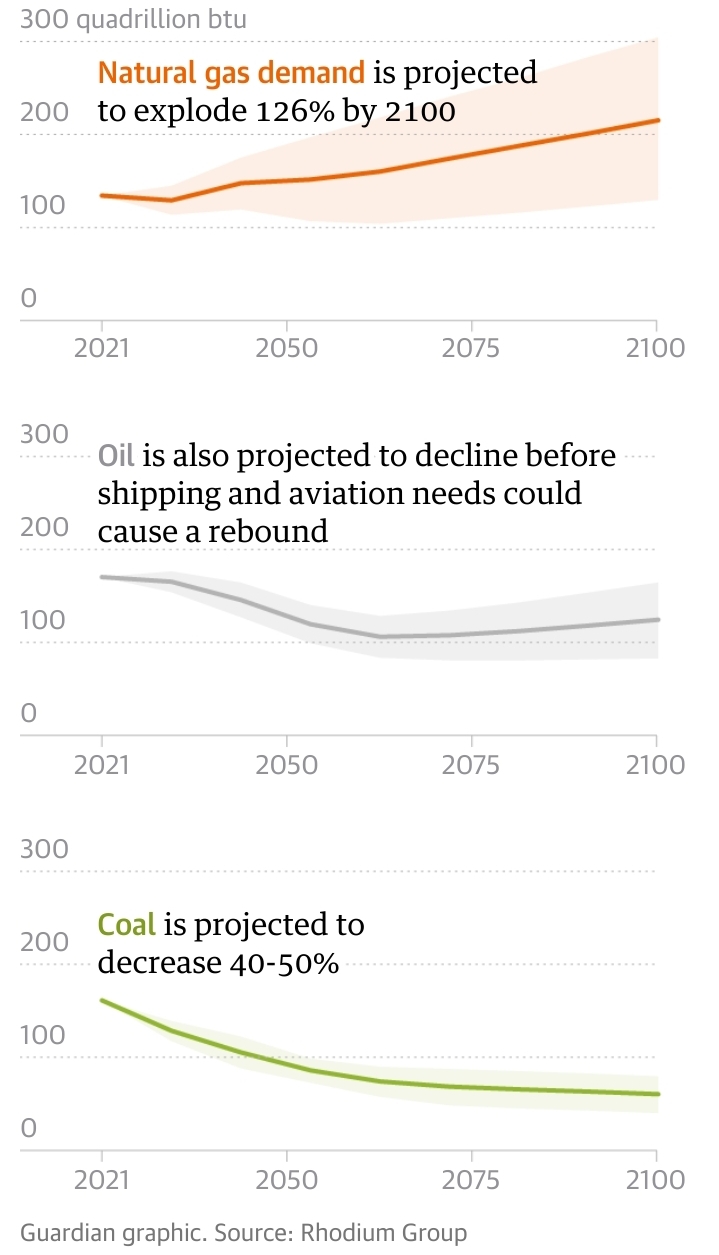
I like this graph from the article:
Wasn’t it 2028 when the carbon budget for 1.5 °C runs out? And 2050 or so for 2 °C? Lol
The dates on which budgets run out depend on the rate at which we continue to extract and burn fossil fuels.
Future projections depend enormously on policy. Change policy, and those curves change.
You are correct with both points. I merely wanted to point out, how far we are from reaching the Paris Agreement.
1.5 may or not be a little later than 2028. The fossil consumption lines may or not be a little flatter.
Maybe out in a limb here but, I think industry and aviation are two of the areas that should be able to use fossil fuels longer than others. Their energy expenditure is huge, yes, but the scientific advancement that is necessary to make them zero carbon are still quite a ways in the future.
It depends on the industry. We know how to prevent the bulk of emissions from concrete and steel, which are the big ones. And yes, aviation might well end up needing to use direct air capture to remove their emissions
Who decides the ‘should be able to’ - do sectors get ‘grandfathering’ rights? Maybe energy-inefficient sectors should decline to give more space for smarter solutions. Much aviation could be replaced by faster rail or shipping, which is much less energy intensive. Many (not all) industrial products also have substitutes. Much concrete and steel is used to make unnecessary roads which cover green spaces, and in the case of China, blocks that nobody even lives in. Many agri-chemicals are over-applied, leading to water pollution.
… each of which is its own massive chunk of the pie.
What a surprise! - decades ago it was obvious these are toughest nuts to crack, which is why I avoided taking planes since 1990. Led me to discover many interesting places on the way, although became isolated from a society which treats jetting about as standard.
By the way, article a bit simple, agricultural sector also has challenges to reduce emissions.
