- cross-posted to:
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- cross-posted to:
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
cross-posted from: https://midwest.social/post/18380473
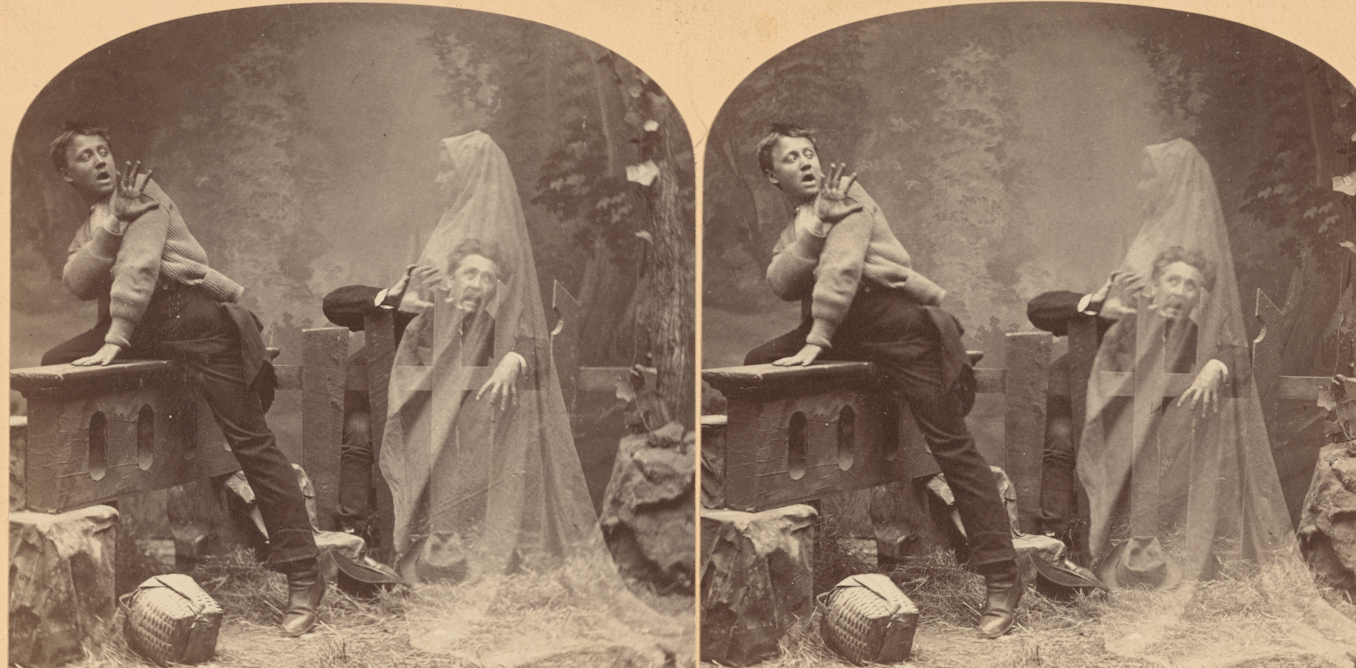
October has long been associated with ghosts – from ancient Celtic festivals to ward off restless spirits after harvest time to the modern standby of using an old sheet to make a last-minute Halloween costume. In the middle of the 19th century, however, popular portrayals of ghosts became a year-round staple, in part because photographers discovered that they could depict them.
The first ghost photographs were accidents. Early cameras required 30 seconds or more to take a photo. If someone wandered briefly into the shot, the resulting picture would contain their ghostly trace superimposed over substantial furniture, buildings or people who had held still for the full exposure.
When shrewd photographers realized that the inconvenience of long exposure time could become an asset, detailed directions for creating these illusions proliferated. Photographers could cut ghost figures from transparent material and place them onto glass negatives or inside camera bodies. Or they could make real people half-transparent through tricks of double exposure.