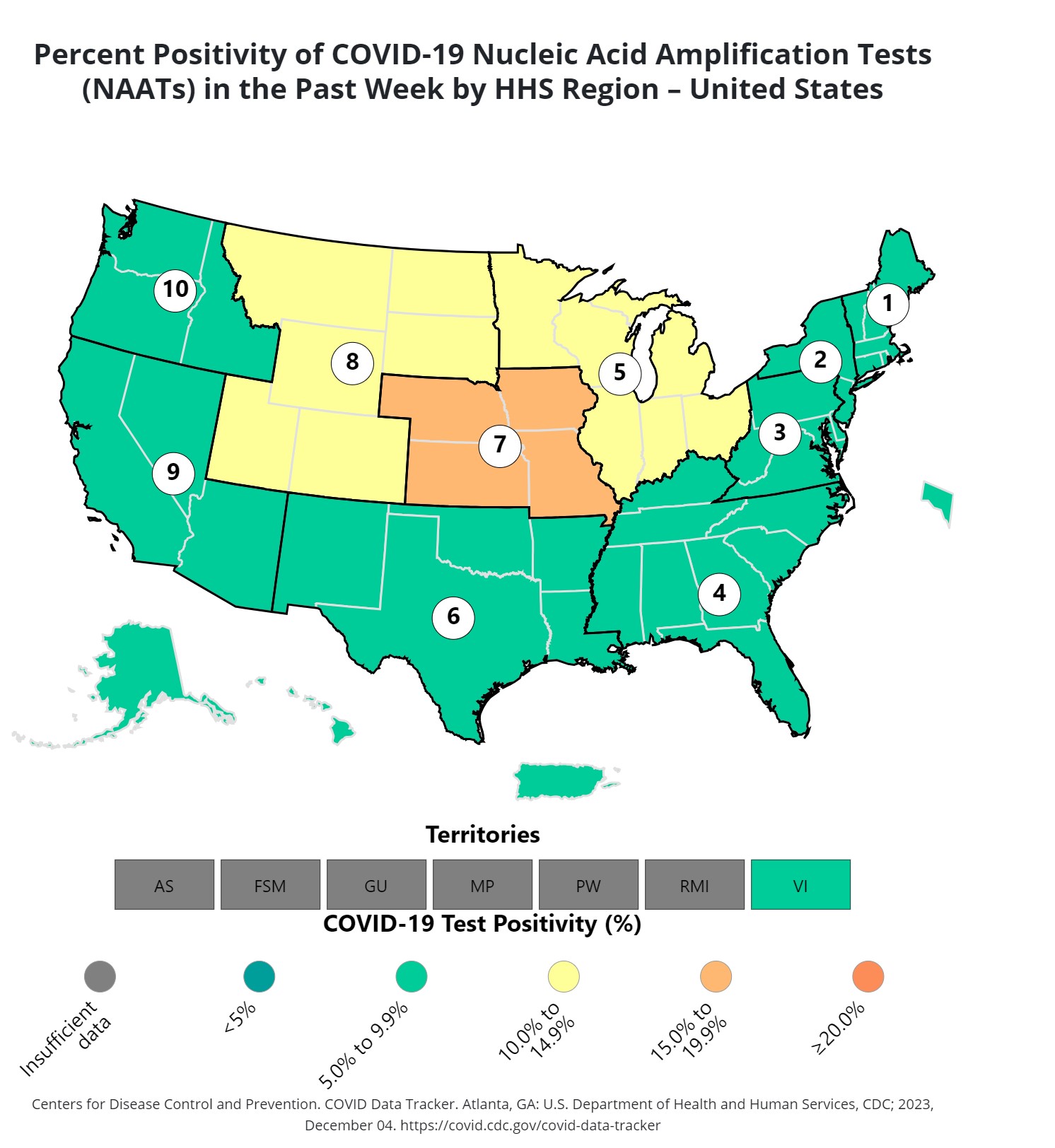
Shocking that areas with low vaccine rates are continuing to see larger outbreaks.
There’s a lot of southern states that have remarkably low positivity rates. Their vaccination rates can’t be very good there, so I’m a curious what the story is there.
Poor reporting. Remember Florida fudging its numbers?
Not sure there was much to that surprisingly. The woman who reported it, Rebekah Jones, is completely batshit.
Just check the waste water data and find out if the concentration of covid is high
It’s still warm and people are still going outside.
Were you living in the South during the outbreak, or purely speculating?
I lived here the whole time and that person is correct.
However my anecdotal experience is most people are refusing to test. Can’t get positive if you don’t test. 😩
I live in arkansas, and i had covid last month. I did a home test, but its not like i reported it to anyone except my work, and family…
The 5G chip implanted during vaccination updated the government once you were infected. No worries.
Many people had COVID and lived and thus acquired immunity. I vaguely remember reading something along these lines during the last year’s sick season, that the total immunity is actually much higher since it’s a combination of immunity through immunization plus immunity after actual illness.
Many people also got HIV and lived… Immunity?
Found this data for people who got the booster. Basic takeaway is that rates for the booster are low in general, but especially so for the south and a good chuck of flyover country.
I would guess then that we’re gonna see infections spike in southern states come January. By then it will be cold and Christmas and New Years will have happened.
https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#vaccinations_vacc-people-booster-percent-pop5
Edit: found a map covering more than just boosters. Same apparent trend overall as the booster map.
https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/us/covid-19-vaccine-doses.html
Yay, I’m in Kansas. My state is winning the race to 100%!
/This is a joke if it wasn’t clear. Someone help make this state sane please 😵💫
There’s several factors involved. One is weather. Another is population density. Others, of course include vaccination rates and efficacy, public use of PPE, and how contagious the particular viral strains circulating in that area at that time actually are.
Basically, every viral transmission is a function of physics and biology. If you take the covid virus, for example, you have a dose dependent relationship. I like to think of it as the 3 D’s: Dosage = Droplets + Duration. We’d say that the probability that a given person would get infected on the basis of a given interaction with an infected person would be a function of virus containing droplet density (ie how many tiny, virus containing spit particles are floating around you, which would decrease as a cubic function of (another D) Distance from that person. Any given virus like that would have a dosage threshold - a number of viruses necessary to cause an infection), which will itself depend on the individual strain and the target’s immunity level vs that variant. The duration part is just to make sure we write it as a function of time - so the cumulative number of viruses you inhale, for instance.
So conditions that tend to increase duration and decrease distance would tend to push infection rates up, but that’s in turn going to be bounded by things like PPE, which work by reducing droplets. And the number of droplets necessary to cause an infection will increase based on the target’s immunity profile.
All of which is to say it’s going to shift around, and the areas with higher (recent) vaccination rates and higher PPE usage will have lower values than they otherwise would have, but because things like population density vary so much between states, it’s going to throw off your analysis if you don’t account for that.
Me an intellect: yes that’s what the map is supposed to do.