- cross-posted to:
- pinball@lemm.ee
- cross-posted to:
- pinball@lemm.ee
First, wear your dust mask. Who knows where these machines have been?
This guy’s channel is great!
Glad to hear that! Yep he’s got a sense of humor -and- knows his stuff.
I’m always so excited every time he puts out a new video. Granted, it took a while for him to discover his humour but it’s very dry and often self deprecating which I appreciate
Pretty sure he’s a Mastodon user, too.
He’s got a bit of an obsession with light bulbs. I love it.
AND heat pumps!
If it doesn’t have a thermal conduction cycle I’m not interested.
Analog computers are pretty cool, yet underrated tech. Although they aren’t very flexible compared to digital computers in the range of what they can do, they do their specific use case very well.
Need to solve a partial differential equation in real time? Don’t bother with iterative algorithms, that’s fool’s math, playa. Just hook it up to an analog computer specifically designed to solve that PDE type, rig up some wires for the input and output to your oscilloscope for real time mathz.
The old firing computers from WW2 are cool as hell.
Not just analog, but mechanical analog.
They take 25 inputs, some of which come directly from the spotter scope things, some from the ship itself, and then controls the guns directly.
It’s all cams, gears, reciprocating whatsits and stuff.
And because it’s analog, there is no quantisation, rounding errors, floating point errors. It’s continuously and instantly calculated.
Very cool stuff.
https://youtu.be/s1i-dnAH9Y4Very pretty stuff. I particularly recommend Ken Shirriff’s Reverse-engineering the mechanical Bendix Central Air Data Computer:
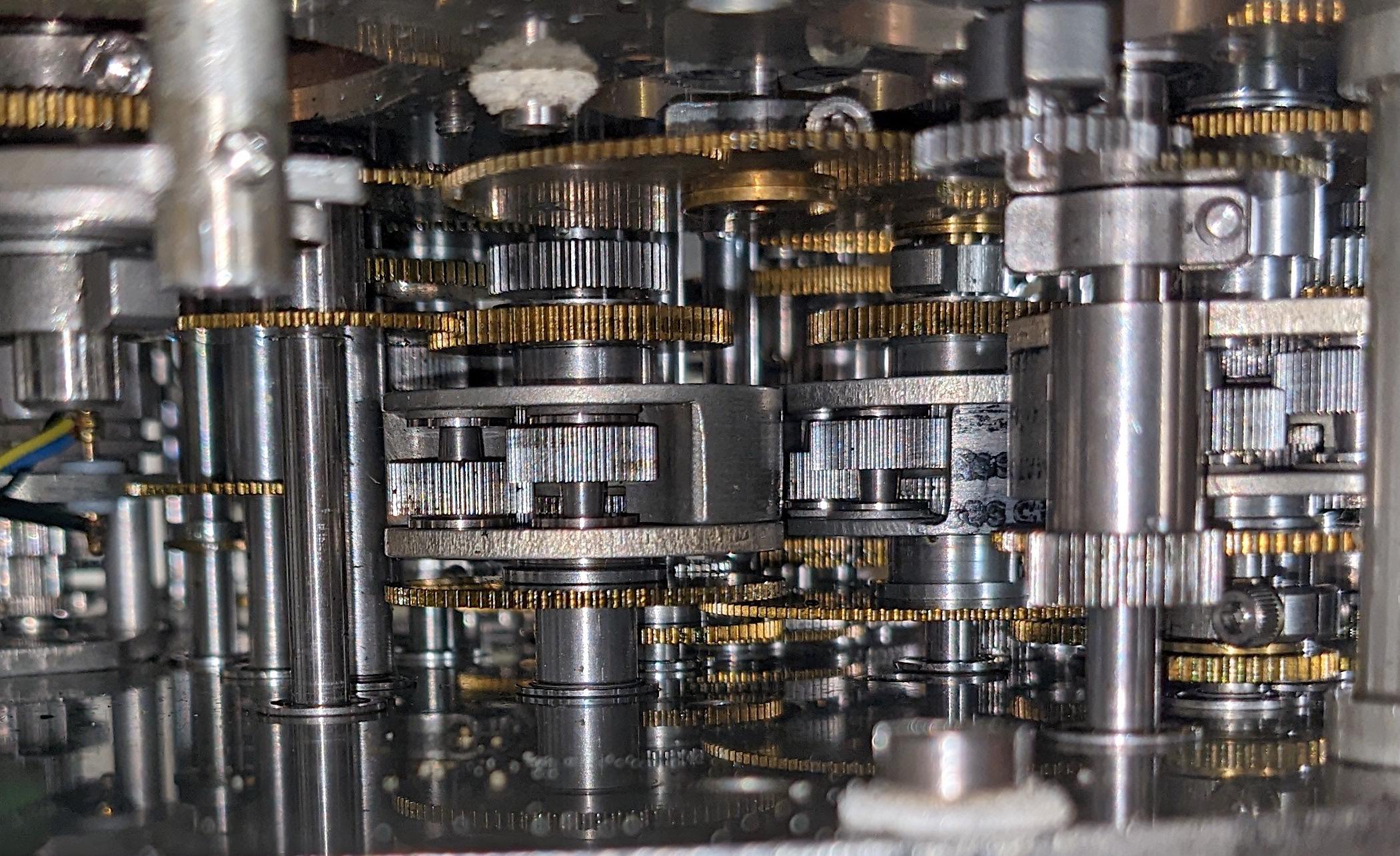
He goes into detail about how non-linear equations are implemented using shaped cam gears (and how such functions can be difference-encoded against linear forms). It’s insane.
And because it’s analog, there is no quantisation, rounding errors, floating point errors.
Eh, I’d say that runout and stiction are their own demons with potentially more bias than those error types :) Not to mention temperature sensitivity – hot days will give different answers to the equations!
Eh, I’d say that runout and stiction are their own demons with potentially more bias than those error types :) Not to mention temperature sensitivity – hot days will give different answers to the equations!
Ha, oh yeh. Good point.
A bit of dirt throwing off the calculations.
Wow, thanks for the link.
The older I get, the more I appreciate things like this, what is basically 19th century mechanical engineering, and what those geniuses were able to do with it. Like fly planes through WWII.
Yeh, it’s crazy right?
This is all just fancy wheels, turned around, odd shaped, made to fit together better.
And the understanding of mathematics, geometry and mechanics makes this massive apparatus of intricately connected pieces - which are relatively easy to understand in isolation - into this thing that can point a gun to be able to hit a moving target.World War 2 was horrendous. But some of the tech developed is jaw-dropping.
Since then, it’s grown exponentially. We are standing on the shoulders of giants!The craziest thing to me is they didn’t have any sort of CAD, 3d printing or other rapid prototyping tech. Most of these things wouldn’t work if made from a cheap sample material either, due to the torque they needed to handle. So really the only option was to put a ton of effort into design, make a few prototypes and start manufacturing. Iterative design could take years to get results back from users.
The classic example to me is the square bale knotter. A collection of cast iron sector gears, cams, jackshafts, blades and hooks with grippers, flung through their complex cycle in 1/4 second in dirty field conditions. Using arbitrary twine and tension, variable drive speed and a product that can vary from 10lbs to 80lbs per volume. For tens of thousands of cycles with minimal maintenance aside from pumping grease into the grease points.
And mine is still working perfectly today after 60 years or more! This year it didn’t miss one single knot of thousands. Incredible engineering.
Part of the
suctionsolution was to simply over-engineer things, which is why old anything mechanical is seriously robust.Looking at cars, an A-arm from a 1950’s vehicle can easily weigh 2x-5x more than in a similar new vehicle.
Good point. I run a lot of old equipment and compared to what new stuff could handle, I absolutely abuse it.
My flatbed “1-ton” F350 used to be a grain truck. 1 ton of grain wouldn’t even fill half the box.
I can put 4 round bales on the deck, well over 2 tons, and the overload spring pack isn’t even touching the mounts yet. It was overbuilt, all right.
Oh yeh, things like old looms? That ran on punch cards to program the pattern?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jacquard_machine
First prototyped in 15th century.
And all the iterations on it in the 18th and 19th century. Very cool tech
IIRC, when they were looking at refitting the Iowa class ships in the late 70s/early 80s, they found that while they could make the mechanical fire control computers smaller, they couldn’t make them any more accurate.
I mean, that’s 40 years ago.
I can understand that their mechanical abilities had peaked, and weren’t able to improve on it.
It would be curious to test that against a modern CNCd mechanical analog firing computer, and then test THAT against a modern 128-bit fixed/floating point computer.
I imagine the computer would win
Here is an alternative Piped link(s):
https://piped.video/s1i-dnAH9Y4
Piped is a privacy-respecting open-source alternative frontend to YouTube.
I’m open-source; check me out at GitHub.
“CuriousMarc” on YouTube has a couple videos where he takes apart and restores an electromechanical navigation computer from an old soviet Soyuz capsule. It could show you exactly where in your orbit you were and calculate rendezvous and reentry burns, all with just a shitload of gears and things. It was incredible.
Isn’t that what FPGAs are for?
Are FPGAs particularly suited to solving PDEs? I just did a search and there seem to be some papers discussing implementing various PDE solving algorithms on FPGAs, but I’m not sure if it’s a task uniquely suited to them.
Probably not especially. But aren’t they basically wires burnt in circuit, made programmable via (UV?) light.
They’re still digital (a wire is either 0 or 1), which isn’t more useful for this than a regular CPU.
What they do excel in is doing stuff in parallel, because there is no linear list of instructions, everything can happen at the same time (unless you specifically block something until a certain signal is sent).
Maybe you’re thinking of EPROMs? I can’t think of anything else that you’d need UV light for. Even then the UV was used to erase them, not write.
Modern FPGAs don’t use UV light, but maybe earlier ones did? As you say, EEPROMs used UV for erasing before writing again.
…now i’m getting confused. Those chips with the round window in the center, what were they again?
No. Modern FPGAs do not use any UV light or have any windows. For storage they use flash memory (same as what’s used in MicroSD cards, USB sticks and SSDs). Some (most?) require you to provide this yourself externally.
Old EPROM (not EEPROM) storage had windows and needed UV to erase, but that’s decades old. I’m not sure if FPGA was common nomenclature back then (PAL/GAL/CPLD were probably the market).
deleted by creator
Ur so right! Diffy-Q has its uses, but analog was too advanced for us to grok so we had to settle for it. Newton ‘discovered’ gravity, and calculus, then found out how useful calc was!
Non-linear? Hella faster! Nature went with analog long ago. No analog, no music!
Tbf, the pinball machine is not really the same as an analog computer, it uses relays in the same way that a modern computer uses a transistor. There is no continuously variable part, just lots of on/offs.
That guy is younger than he looks. He’s only 30. Quite the “old soul”.
He’s even serious when he makes a blooper. Brilliant.
I can’t wait to watch this having restored an early 90s Williams machine years back. Doubly so with it being a TC vid, his channel is excellent.
I wanted a machine in college but knew I’d have to understand and maintain it with so many moving parts, thus shelving the idea pretty quickly. Years later, I stumbled into an arcade abused cabinet with a decent playfield and had to have it. It was a challenging few months but a decade later it still works great and I’ve grown comfortable with crawling in there. Great forums like Pinside were also a tremendous help, I wouldn’t have taken the gamble without the Internet.
My god, if you understand how these systems work, I’m impressed.
I’m good with DC stuff of this era (switches, relays, etc) and man I have to work hard to visualize these things.
I’m seriously impressed with the engineers who designed these crazy complex electro-mechanical systems.
I have some older relatives who were aircraft engineers back when these types of systems were used… Aircraft up through the 70’s. I’ve read some of their manuals… Staggering complexity.
Well, I’d say I understand enough to get by but I did also grow up building RC cars and later working on electronics/computers, so that definitely helped. That said, there’s been more than a few times I had to break out a wiring diagram and consult with folks online because I was too scared to break something.
With all those noises moving parts inside, playing an OLD machine felt like tickling a hippo.
For those with an interest in pinball, I strongly recommend looking up Pinball: The Man Who Saved the Game. It may be a bit of a predictable, B-rated movie, but it’s a lot of fun to watch and has some good lines. Hulu has it!
I know a guy who works on Pinball machines as his profession. He sells em too.
Really enjoyed Skylab that he repaired. Seeing the way Electromechanicals run everything so…binary…is fascinating
Here is an alternative Piped link(s):
https://m.piped.video/channel/UC48AesDYiJ2UYPaRX5ZLgLw
Piped is a privacy-respecting open-source alternative frontend to YouTube.
I’m open-source; check me out at GitHub.
Did i miss where he explained those two big wheel-switch thingies?
Here is an alternative Piped link(s):
https://piped.video/watch?v=ue-1JoJQaEg
Piped is a privacy-respecting open-source alternative frontend to YouTube.
I’m open-source; check me out at GitHub.
That’s SO cool! It’s like those extremely complex redstone builds in minecraft, but irl and way cooler. I love it!
Apologies for hijacking the thread, as I understand my comment is only tangential towards what is being discussed, but if you love pinball machines it’s such a great link to take a look at, so I thought I would still share it with you all.
I’ve been there!! Amazing spot to play pinball, just wish they served beer… I’m pretty sure they have over 200 tables and some fairly rare ones. Bonzai Run, and Water world are 2 that had fairly limited runs but can be played there.
I have to say I think his studio lighting isn’t doing him any favors. In the first segment he looks so much better. Maybe it’s different cameras.






