In short:
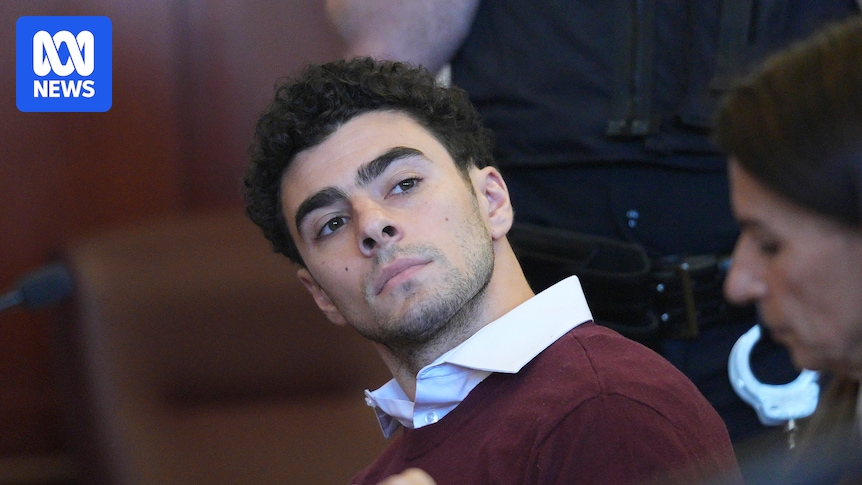
Luigi Mangione has pleaded not guilty to state murder and terror charges.
Mr Mangione is accused of killing UnitedHealthcare CEO Brian Thompson outside a Manhattan hotel.
What’s next?
Prosecutors say the state case is expected to run parallel to a federal prosecution.


How would you describe the difference between just and unjust without a reliance on a higher power, andcalso accounting for the fact that ‘what is moral’, while often similar across the world, isn’t always the same.
In other words, would you have an interpretation of the same concepts, but able to be applied more universally?
That’s a great question. MLK is absolutely appealing to a higher power in this letter, which you’re picking up on. Pretty much anything under the “natural law” perspective sort-of requires that belief. Some try to go without it, but it’s rare in this branch of philosophy.
I also think it’s notable that just about every “western” legal system in some way sits on the ideas of natural law ethics (either through Thomas and Augustine or Locke, etc… and there’s a lot of variation there. Thomas and Locke have very different ideas about property and individual good, for example). I think it’s important to wrestle with that, especially in our pluralistic societies that can’t impose a belief in said higher power.
But, back to your question. I’m not personally a natural law thinker, mostly because I chafe at the idea of law to begin with. It just doesn’t quite square with my more anarchist tendencies. So, I’m less interested in “just” and “unjust” and more in what makes something wholly “good.”
On that front, I borrow my definition of good from a guy named Ivan Illich: something is good when it is uniquely and incomparably appropriate in it’s given setting. This accounts for the situational nature of things, but also for the variance between cultures. There’s also more of a simplicity to asking if something is good then if it’s just. Justice can be hard to define, but goodness is pretty easy and obvious.
It’s rarely good to be hungry, thirsty, and tired, for example; so it’s good to give people food, water, and rest.
If I remember correctly, this definition of the good comes from a paper of his called “Needs.”
Thinking with something like the US healthcare system, we can ask if it’s good (that is, uniquely and incomparably appropriate) to receive lifesaving care. The answer there is an obvious yes.
If we ask if it’s just… then we find ourselves dealing with what people deserve, what can be afforded, and a million other ways of weaseling out of responsibility for doing the right thing.